Clinical Patterns and Prognostic Outcomes of Asian Ocular Adnexal Marginal Zone Lymphoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jh2103Keywords:
Ocular lymphoma, Rituximab, Prognostication, Positron emission tomography, SUVmaxAbstract
Background: Ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphoma (OAMZL) is the most common subtype of primary ocular lymphoma and has been rising in incidence in Asian populations.
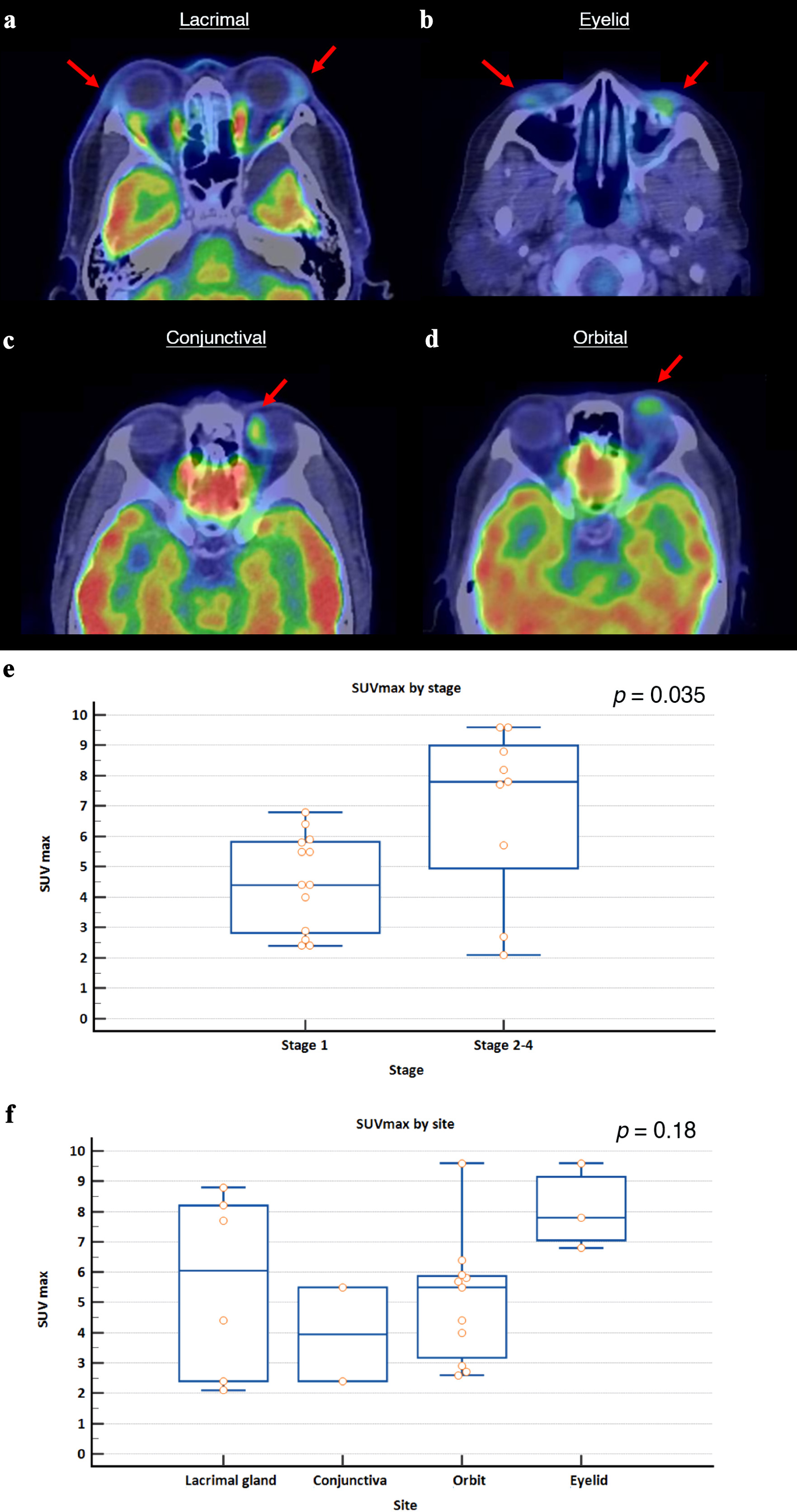
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of 95 patients diagnosed with OAMZL within a multi-ethnic cohort from Singapore. Clinical characteristics, survival outcomes including overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS), and maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) on staging F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18-FDG-PET/CT) were investigated.
Results: The cohort comprised 60 males and 35 females, with a median age of 58 years (25 - 88). Median follow-up was 92 months. The most common sites involved were the orbit (49.5%) and lacrimal gland (23.2%). Most patients presented with stage 1 disease (72.6%). Five-year OS and PFS for the whole cohort were 94.9% and 84.1%, respectively. Factors significantly associated with poorer OS included advanced (stage 2-4) disease (hazard ratio (HR) 6.26, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.69 - 23.19, P = 0.0061), older age above 58 years (HR = 15.29, 95% CI: 4.47 - 52.3, P < 0.0001), and higher mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue International Prognostic Index (MALT-IPI) scores of 2 - 3 compared to low (0) and intermediate (1) scores (HR = 9.28, 95% CI: 1.24 - 69.11, P < 0.0001 and HR = 10.99, 95% CI: 1.34 - 89.94, P < 0.0001), respectively. Older age (HR = 2.41, 95% CI: 1.07 - 5.43, P = 0.0330) and advanced disease (HR = 2.47, 95% CI: 1.07 - 7.03, P = 0.0348) were significantly associated with poorer PFS. Median SUVmax of the lesions was 5.6 (2.1 - 9.6), with significantly higher values in advanced disease.
Conclusions: Our study illustrates the favorable prognosis of OAMZL in an Asian cohort, although particular factors may portend worse survival outcomes.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








