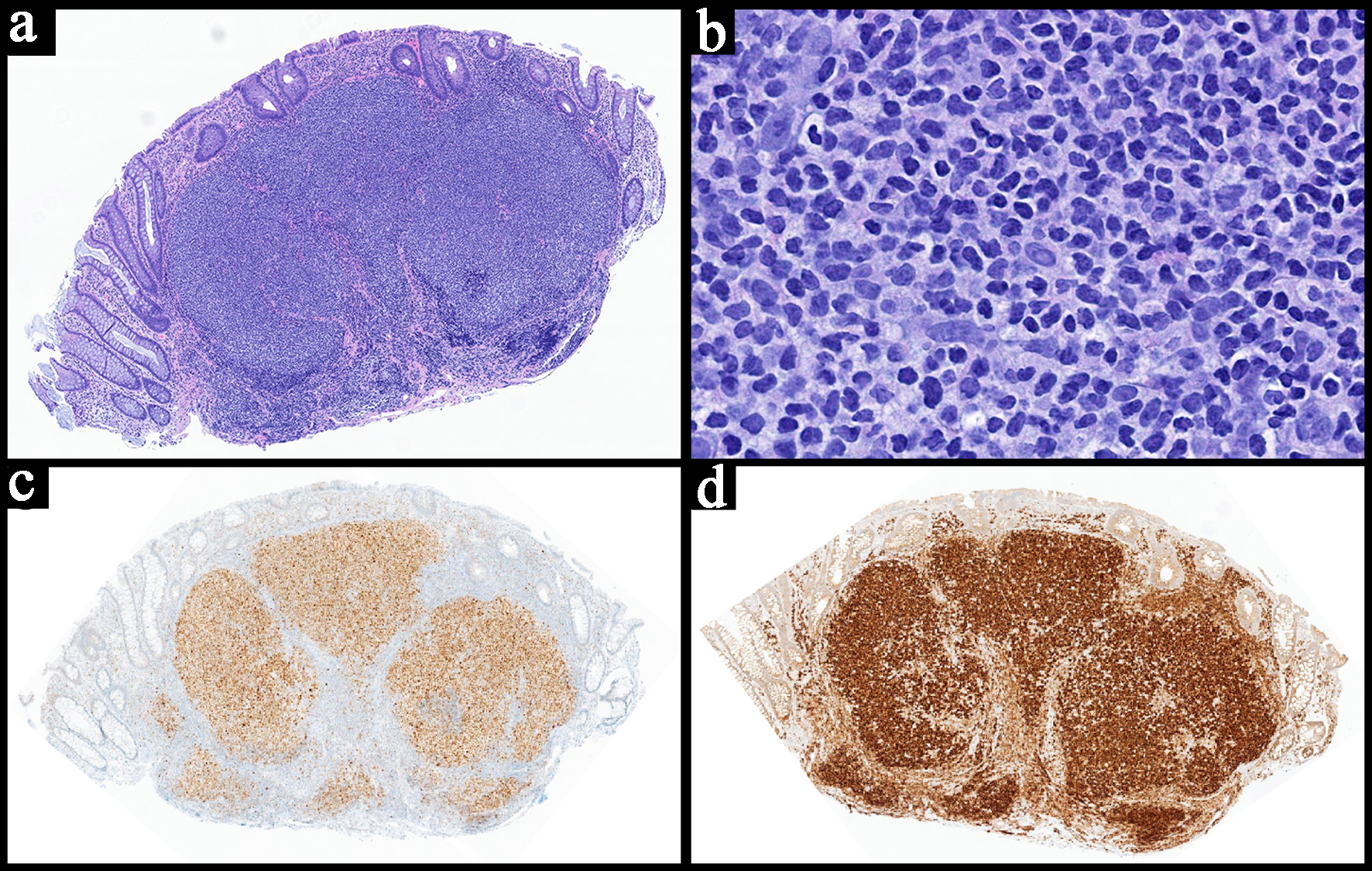
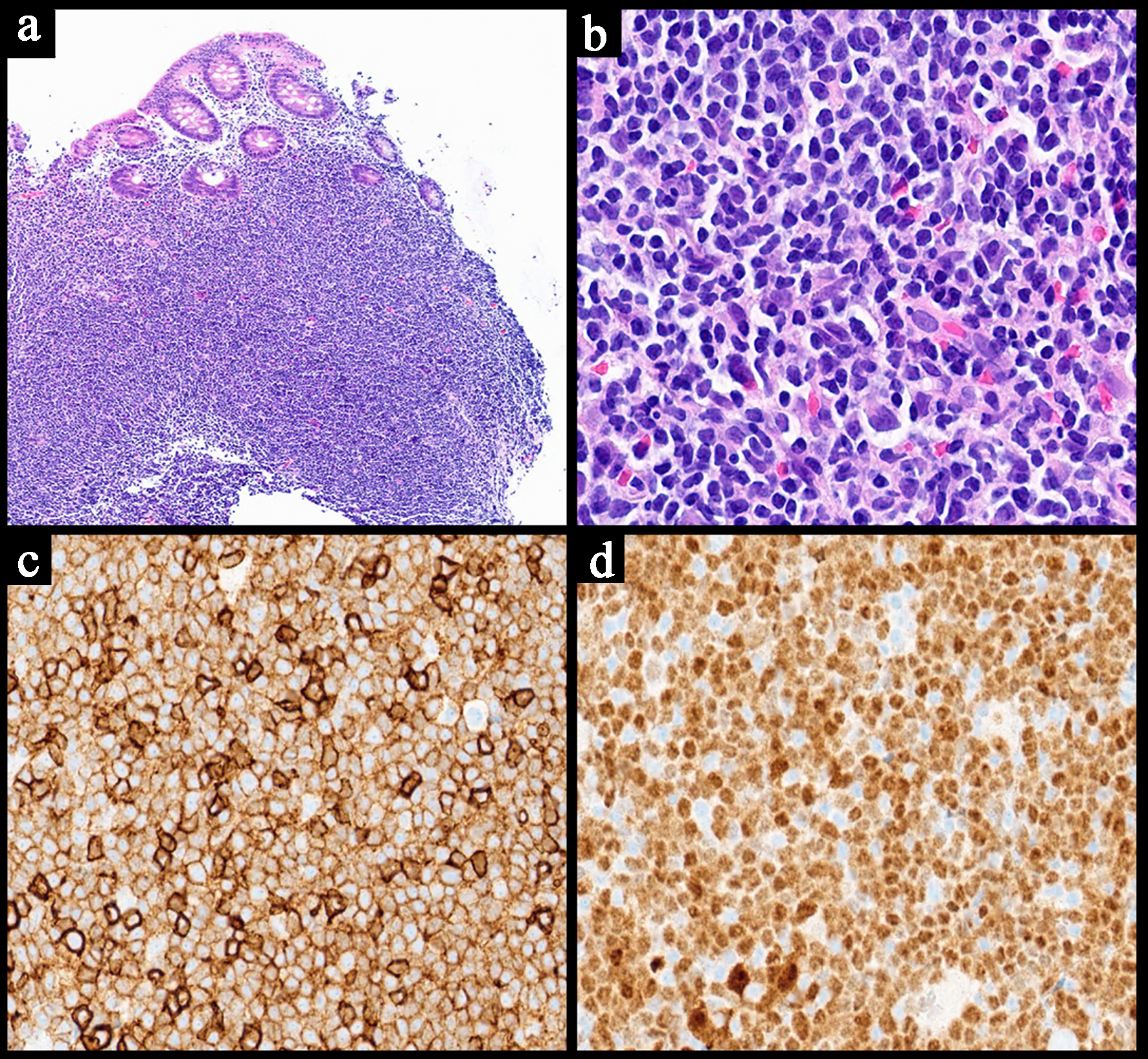
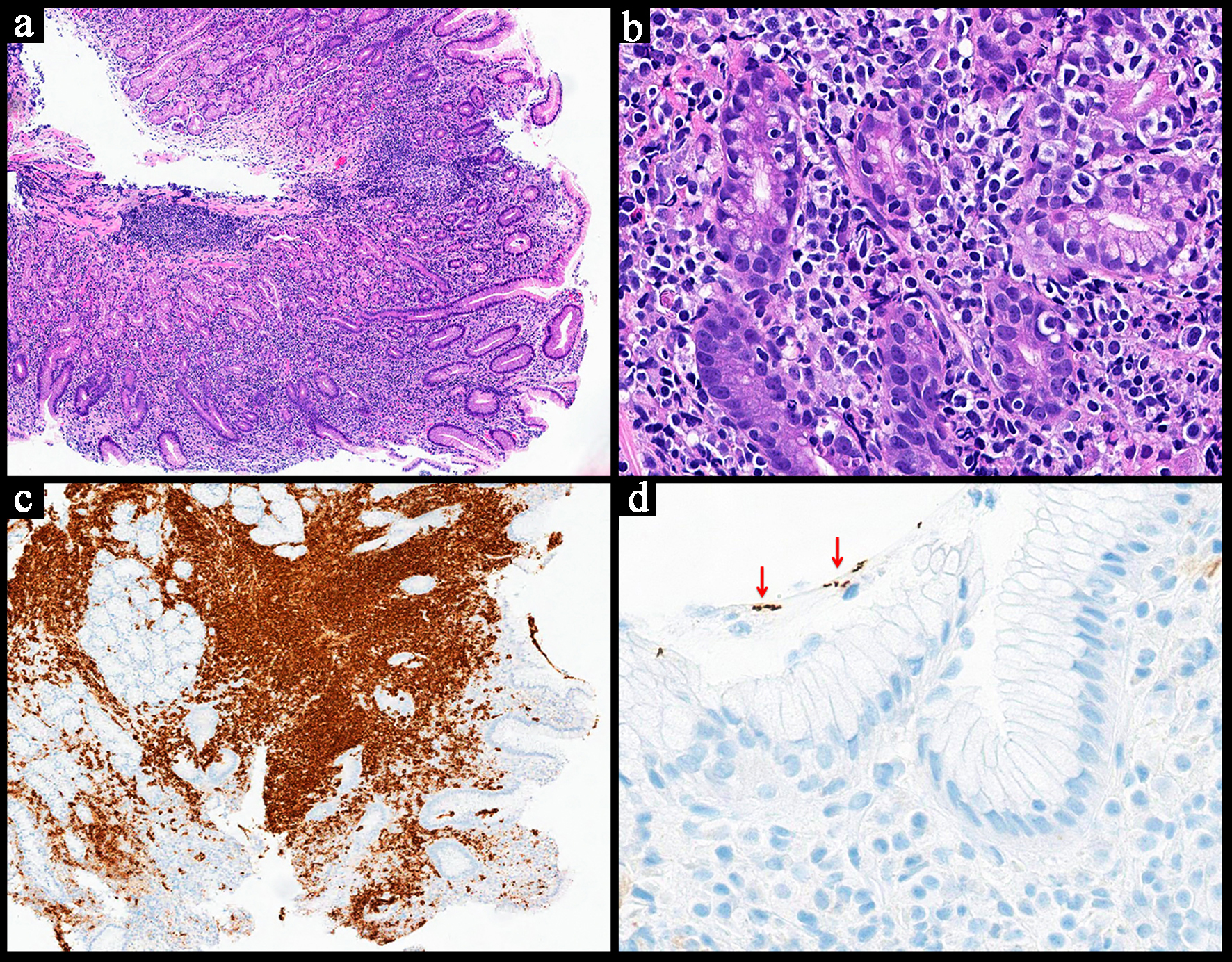
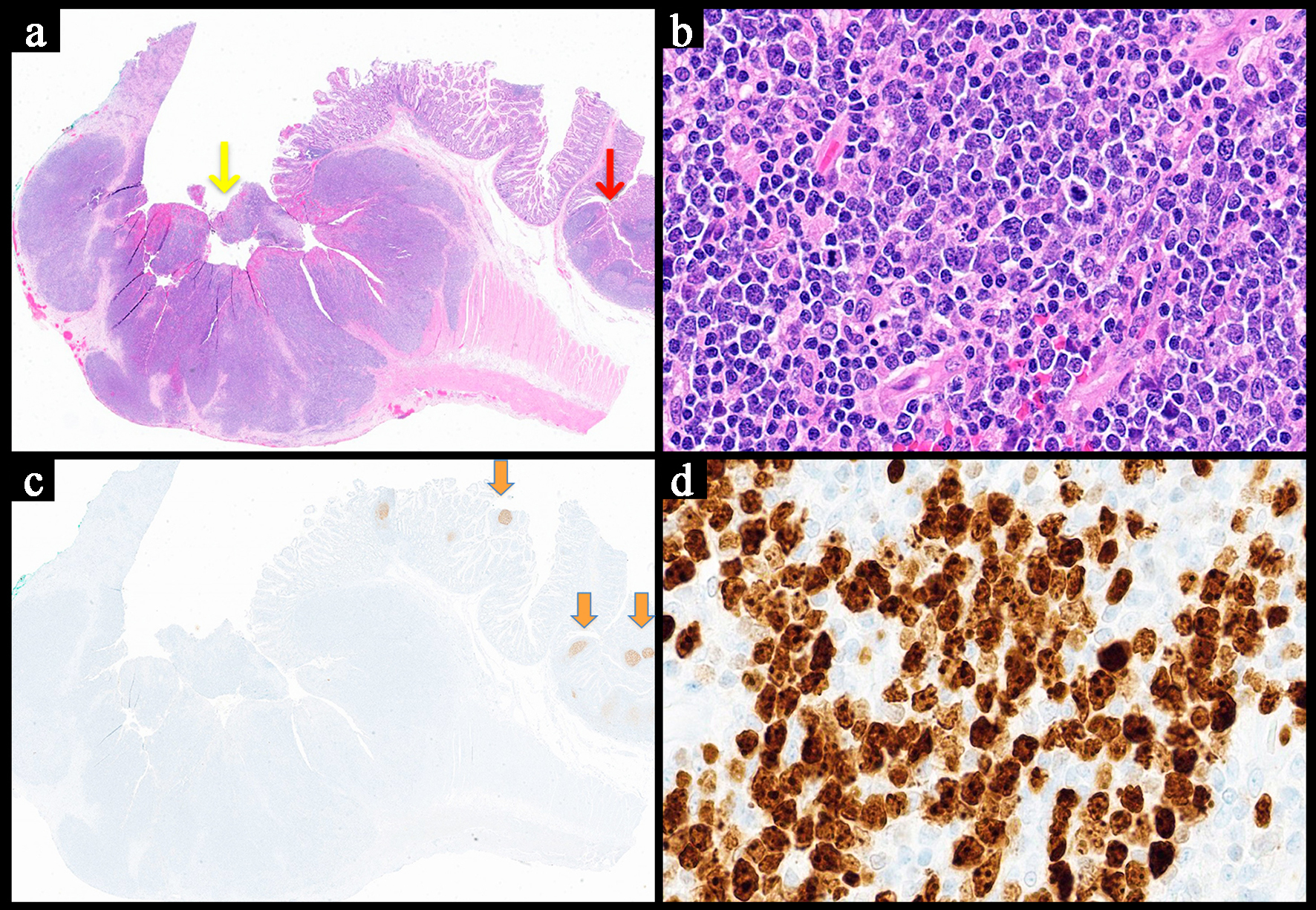
| Clinical presentation | Typically asymptomatic, incidental | Variable, non-specific | Gastric may be asymptomatic; intestinal may have pain/abnormal bowel habits | Variable, non-specific, high rate of perforation | Rapidly enlarging mass, pain, obstruction, intussusception | Diarrhea, abdominal pain, B symptoms | Variable/non-specific symptoms; history of solid/hematopoietic transplant |
| Common location | Small intestine, particularly duodenum | Lower GI tract | Stomach | Stomach more common than intestine | Ileocecal region | Any; colon more common in HIV - patients | Stomach and small intestine |
| Etiological factors/pathogenesis | BCL2 translocation t(14;18) | CCND1 translocation t(11;14) | H. pylori (gastric), t(11;18) (gastric), Campylobacter jejuni (small intestinal) | H. pylori in gastric type; EBV in general | EBV; plasmodium falciparum; HIV; MYC translocation t(8;14) | IGHV rearrangements, MYC translocations, PRDM1/Blimp1 mutations, EBV infection (especially in HIV+) | EBV (mainly); additional: hepatitis C and HHV-8 infection |
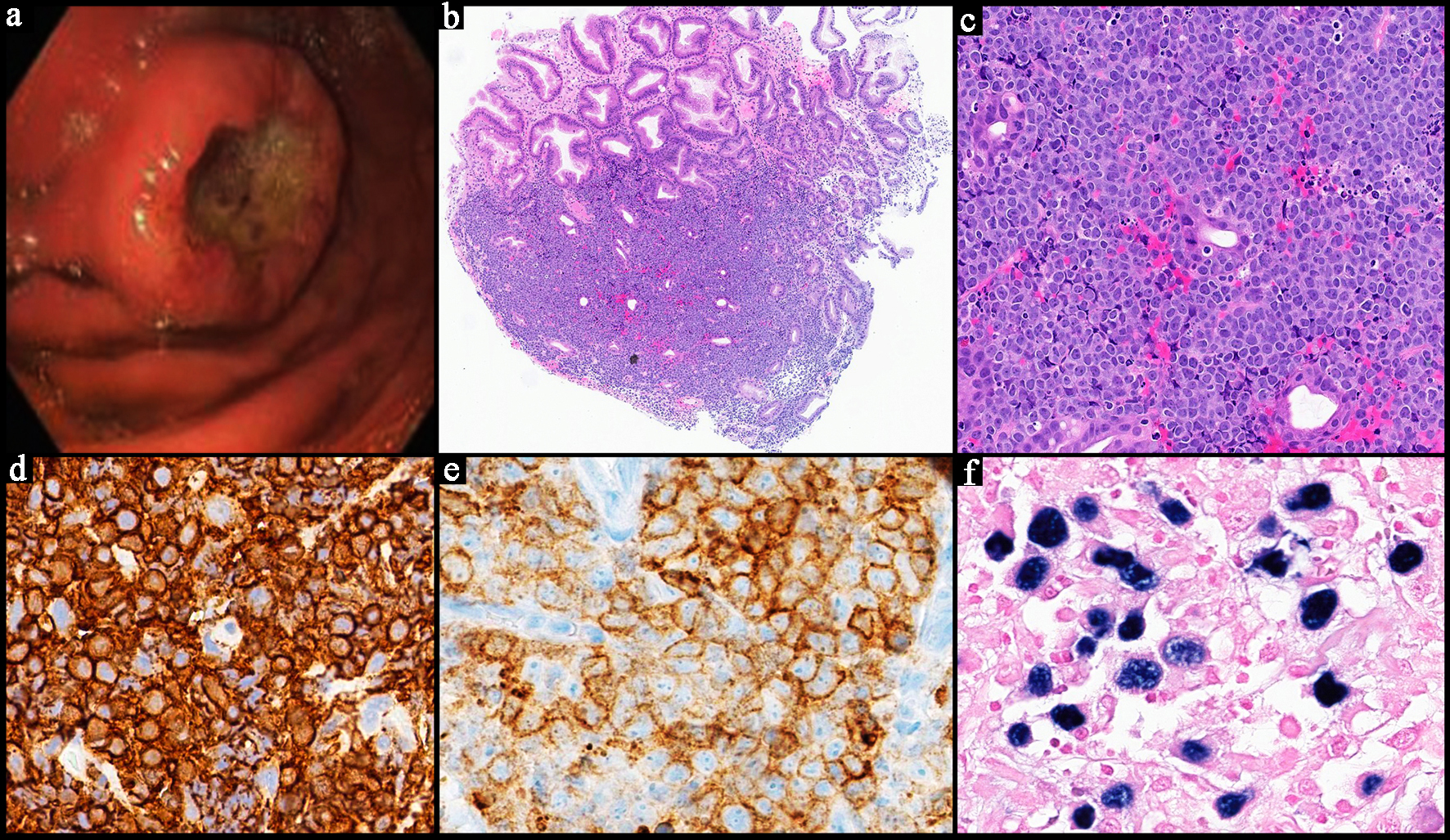
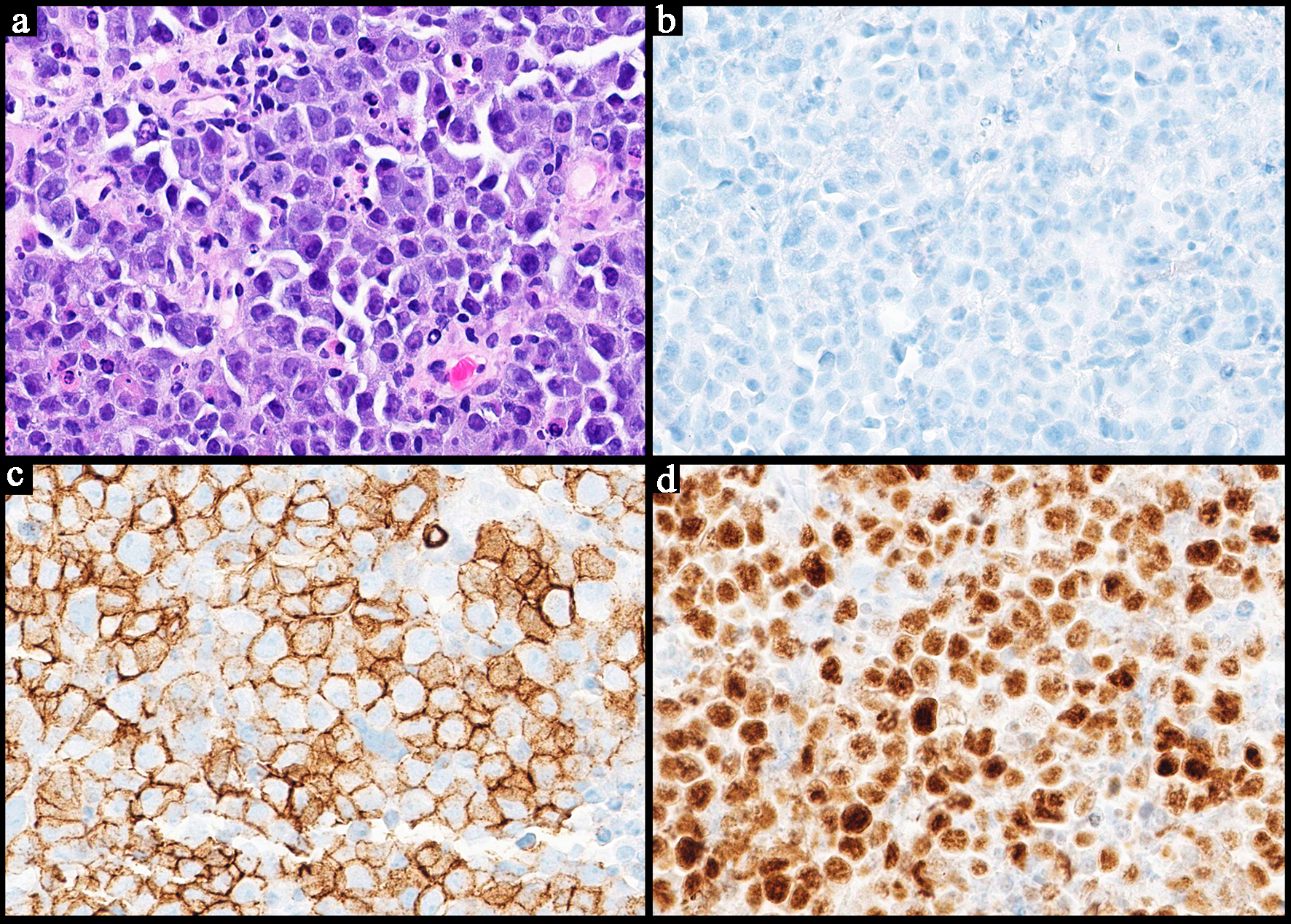
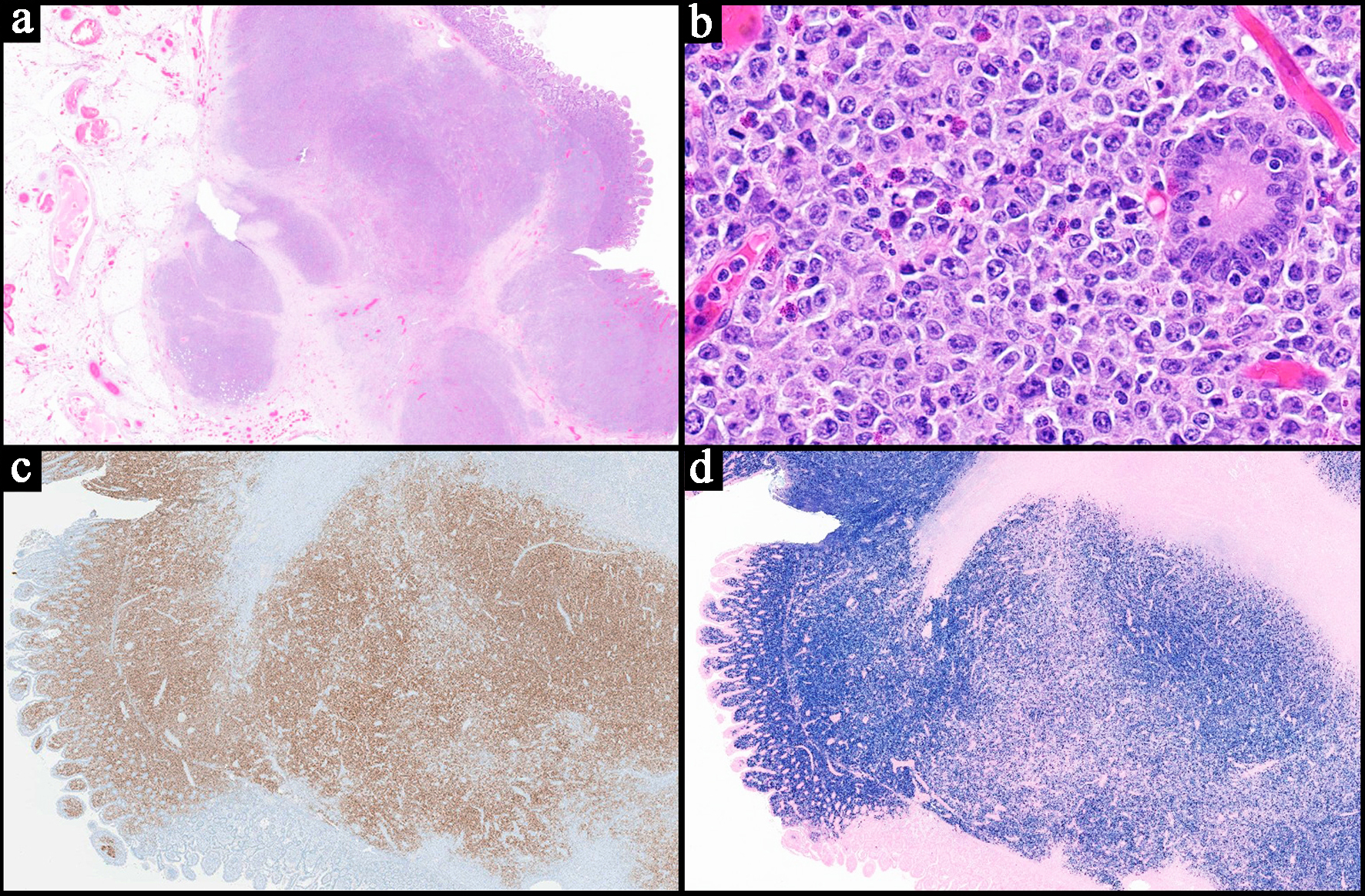
| Histopathology | Follicular or nodular pattern, mixed centrocytes and centroblasts | Nodular infiltrate; small-medium cells | Monocytoid lymphocytes, infiltration of reactive follicles | Sheets of atypical large lymphoid cells, usually centroblastic or immunoblastic | Sheets of medium-sized cells, multiple nucleoli, basophilic cytoplasm, “starry-sky” pattern | Sheets of large neoplastic cells, plasmablastic and immunoblastic morphology | Variable; non-destructive, polymorphic, monomorphic, CHL, mucocutaneous ulcer subtypes |
| IHC | CD10+
CD5-
BCL6+ BCL2+ | CD5+
Cyclin D1+ SOX11+ | CD5-
CD10- | Variable based on GCB vs. non-GCB phenotype; high Ki-67 | CD10+
BCL6+
MYC+
High Ki-67
CD5-
BCL2- | CD38+
CD138+ Kappa/lambda restriction
High Ki-67 CD20-
Weak B-cell markers | Variable based on subtype |
| Treatment | Watch and wait mainly; chemotherapy and immunotherapy | Observation in limited disease, chemo-immunotherapy, novel BTK inhibitors, venetoclax and lenalidomide and auto-HSCT; rituximab maintenance in older patients (not eligible for HSCT) | Variable; H. pylori eradication; observation; surgery; radiotherapy; chemotherapy and immunotherapy | Surgery, chemotherapy and immunotherapy, radiotherapy, H. pylori eradication | Multiagent chemotherapy | Palliation, chemotherapy, HSCT | Reduction of immunosuppression, chemotherapy and immunotherapy, EBV-specific T-cell immunity or donor lymphocyte infusions |
| Prognosis | Generally favorable; better prognosis with duodenal involvement | Intermediate (potentially favorable with newer therapies/HSCT) | Typically indolent | Favorable compared to primary nodal subtypes | Worse in gastric type vs. intestinal; responds well to chemotherapy | Unfavorable, aggressive | Unfavorable |