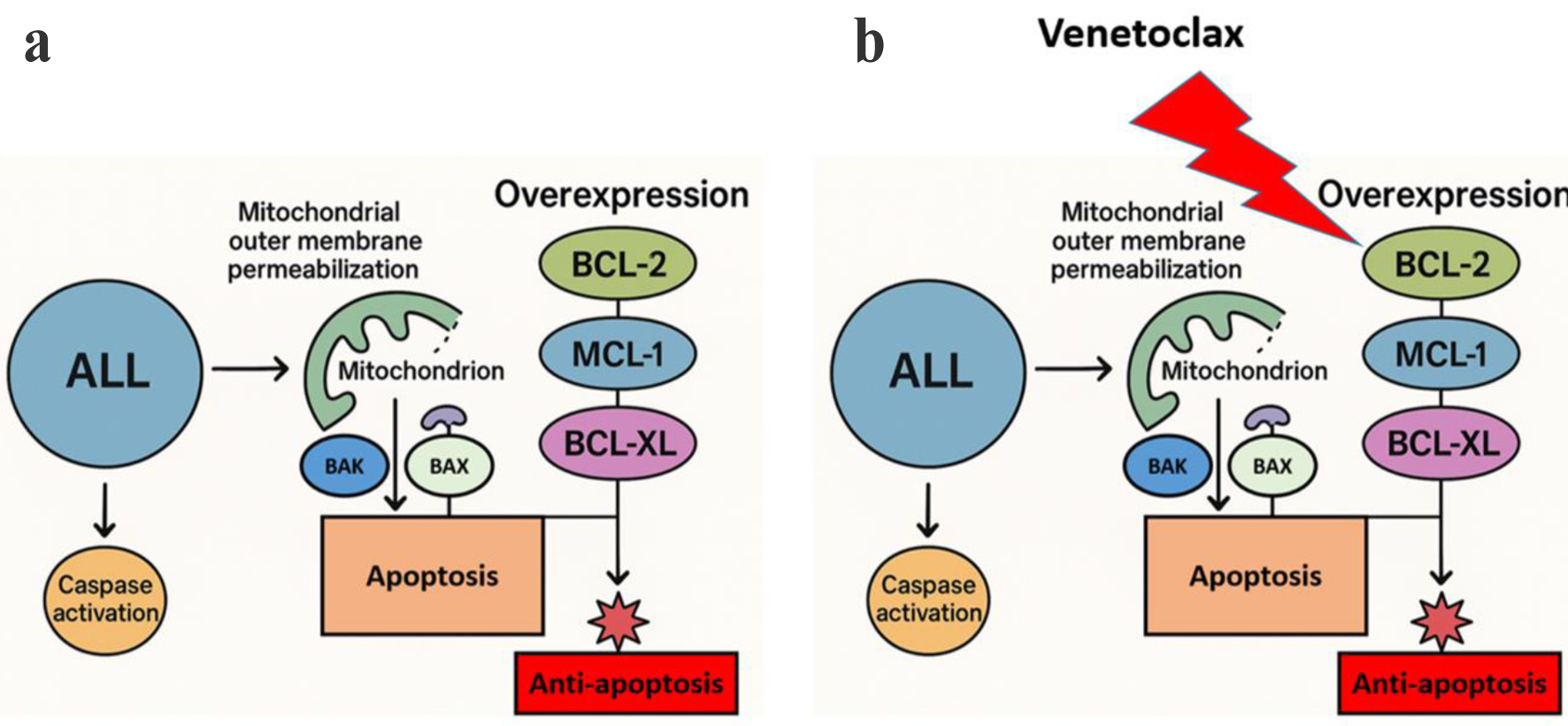
Figure 1. Mechanism of venetoclax-induced apoptosis in ALL. (a) ALL cells express elevated levels of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins (BCL-2, MCL-1, and BCL-XL) which prevent mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) and trap pro-apoptotic proteins (BAX and BAK) to stop caspase activation and apoptosis. (b) Venetoclax specifically targets BCL-2 to enable apoptotic signaling through MOMP and caspase activation. The compensatory increase of MCL-1 and BCL-XL proteins helps to preserve anti-apoptotic signaling which leads to venetoclax resistance. ALL: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; BCL-2: B-cell lymphoma 2; MCL-1: myeloid cell leukemia-1; XL: extra large.