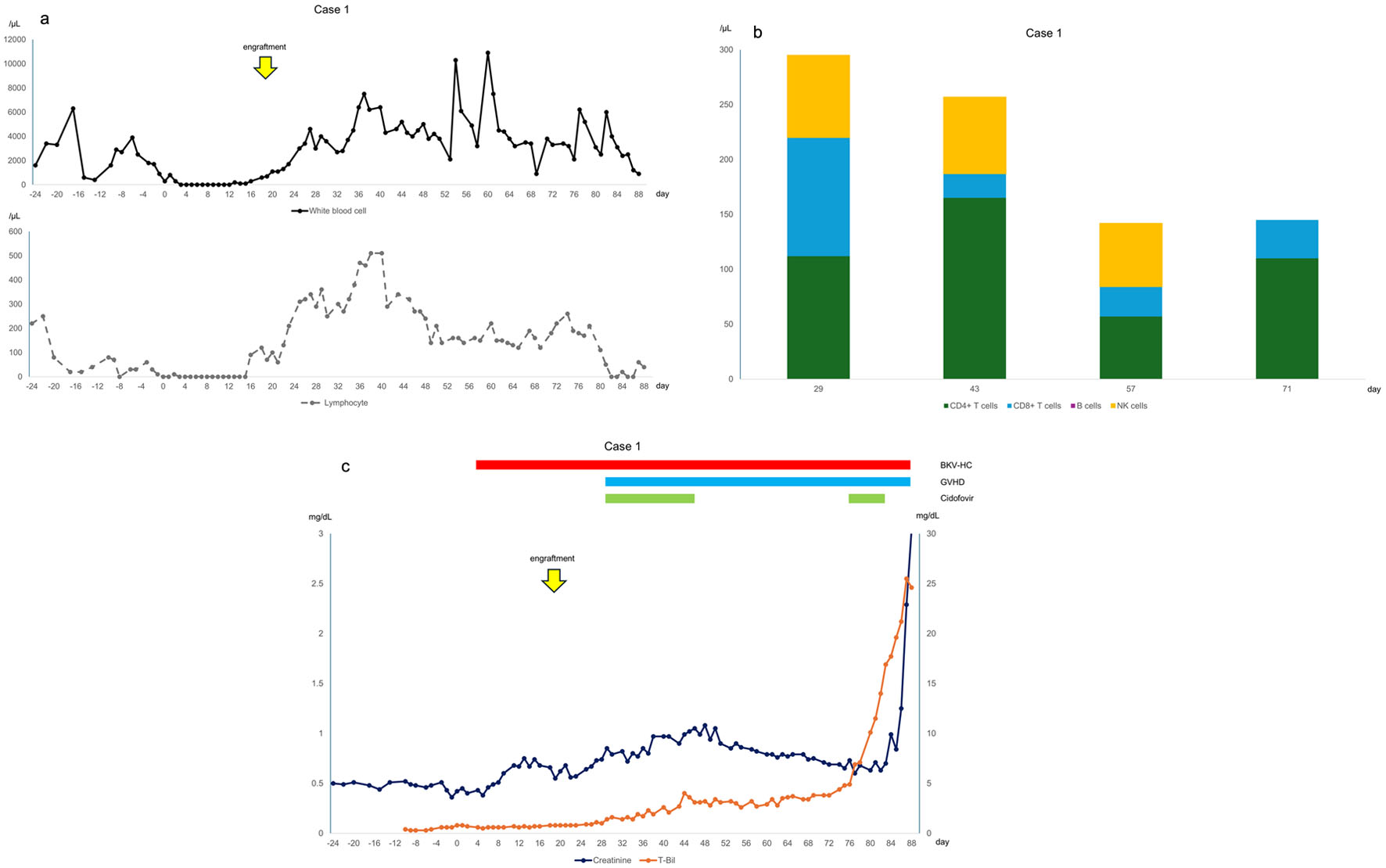
Figure 1. (a) Changes in white blood cell and lymphocyte counts, with day 0 representing the day of infusion. Lymphocyte counts decreased after day 50 when acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) worsened again. (b) Lymphocyte subsets, where CD4+ T cells are CD3+CD4+CD8, CD8+ T cells are CD3+CD4CD8+, B cells are CD19+CD20+, and natural killer cells are CD3CD16+CD56+/CD3CD16CD56+. CD4+ T cells were particularly low on day 57 when acute GVHD worsened. (c) Clinical course of the case, with day 0 indicating the day of infusion. BKV-HC: BK virus-associated hemorrhagic cystitis.
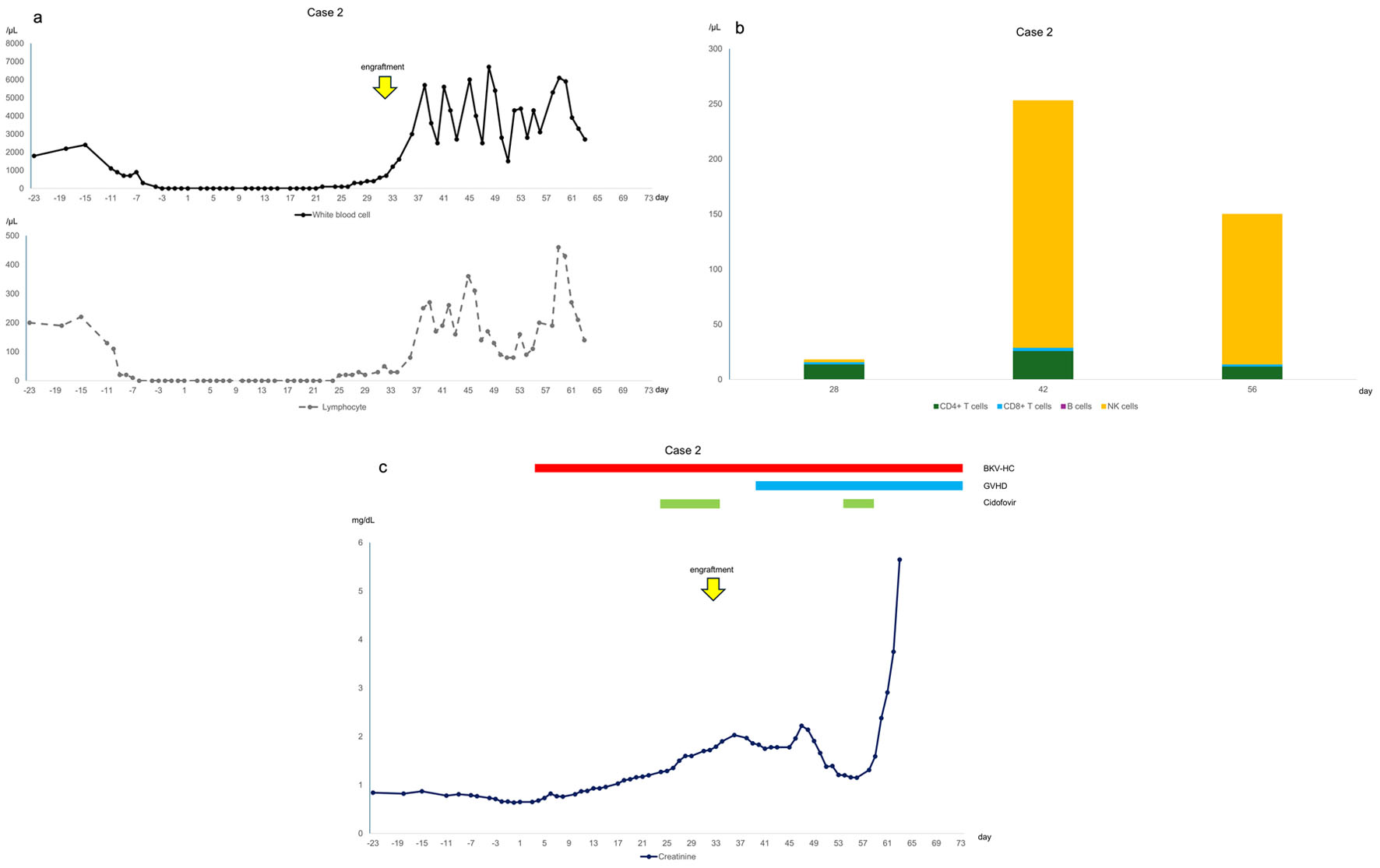
Figure 2. (a) Changes in white blood cell and lymphocyte counts, with day 0 representing the day of infusion. Lymphocyte counts were lower than those in case 1. (b) Lymphocyte subsets. The absolute numbers of CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells were lower than those in case 1. (c) Clinical course of the case, with day 0 representing the day of infusion. Creatinine levels increased with the worsening of acute GVHD on day 40.
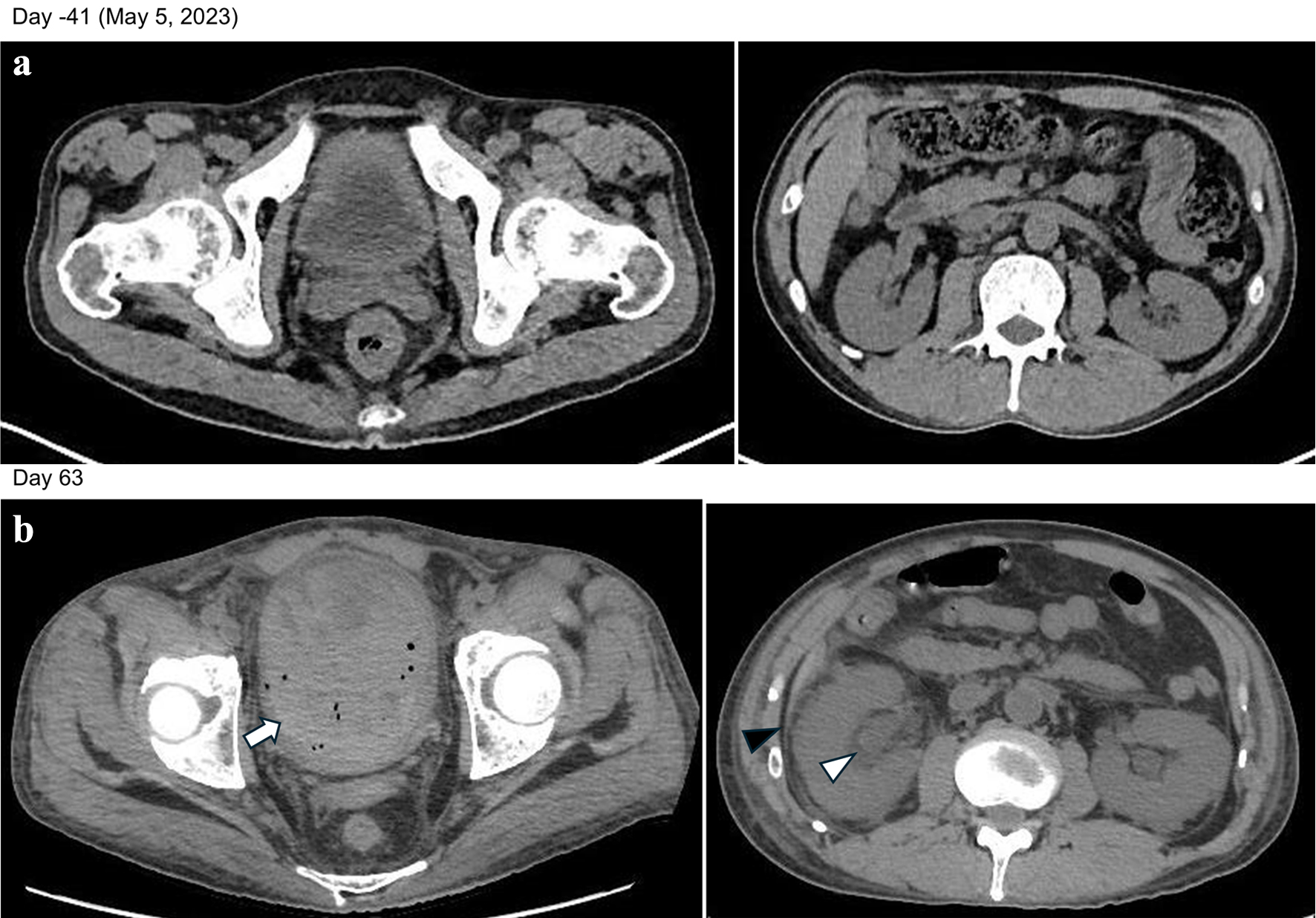
Figure 3. (a) Findings after the completion of three courses of Pola-BR. No abnormal findings were observed in the kidneys. (b) Heterogeneous high-intensity areas in the bladder, indicating hemorrhage and blood clots (arrow). Dilation of the renal pelvis (white arrowhead) and increased density of perirenal fat tissue (black arrowhead) were observed. These findings indicate that the BK virus infection had spread from the bladder to the kidneys.


