| Methodology | PCR-based strategies: e.g., ASO-RQ-PCR. Immunophenotype-based strategies: MFC for immunophenotyping | NGS-based clonality assays: high-throughput sequencing of Ig rearrangements provides ultrasensitive MRD detection. |
| Sensitivity | Moderate sensitivity (approximately 1 × 10-5) | Ultra-sensitive detection, capable of identifying very low levels of residual leukemia cells |
| Specificity | Provides moderate specificity through detection of immunophenotypic markers | Identifies specific miRNA patterns associated with distinct cancer subtypes, grades, and stages |
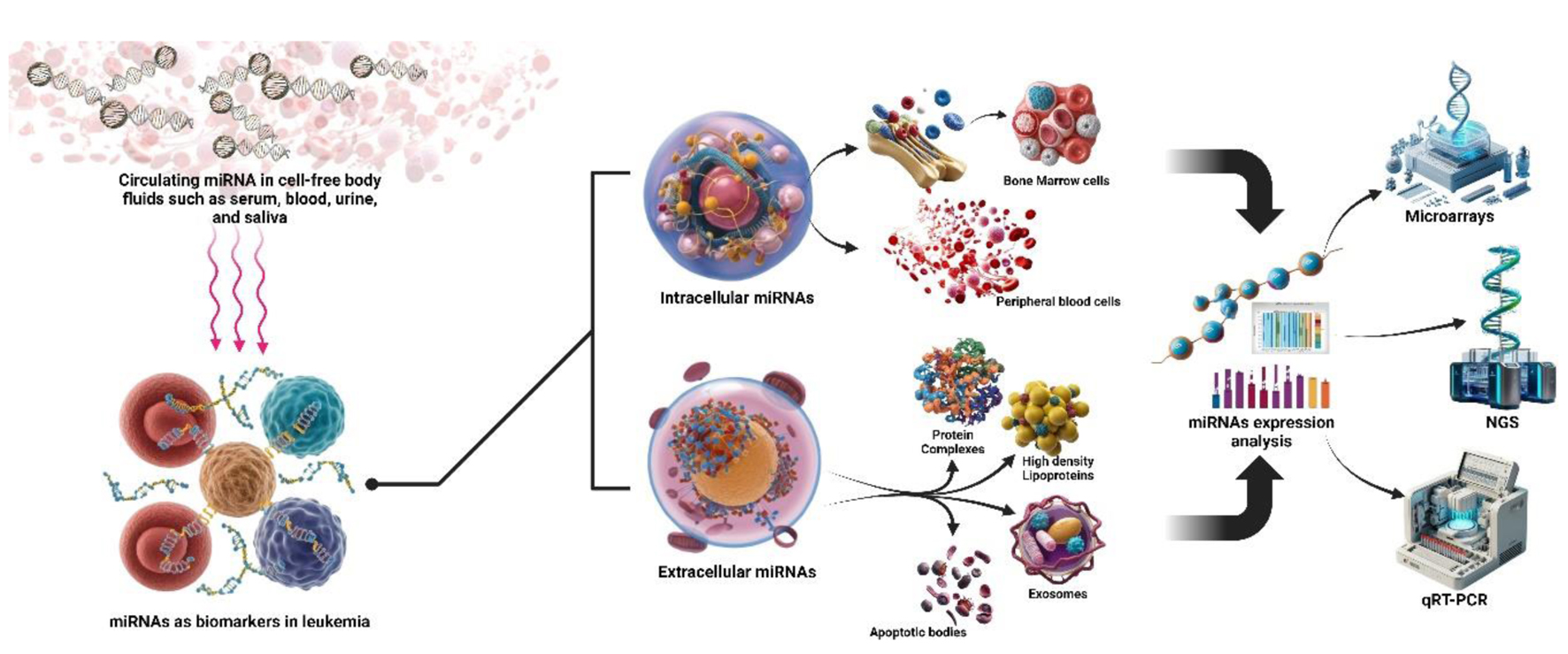
| Sample type | Typically requires invasive procedures (e.g., bone marrow aspirates) | Non-invasive approach using easily accessible body fluids (blood, urine) |
| Clinical utility | Well established in clinical practice for various hematological malignancies | Shows promise for early diagnosis and improved prognosis, particularly in breast cancer |
| Customization | Limited to standardized assays with fixed parameters | Can be tailored to individual patient profiles based on unique miRNA expression patterns |
| Functional insights | Focuses on identifying specific immunophenotypic markers without broader pathway insights | Provides additional information on miRNA networks and their roles in oncogenic processes, such as EMT and cellular plasticity |
| Role in EMT | Not directly linked to EMT | Directly implicated in EMT and cellular plasticity, playing a role in tumorigenesis |
| Early detection | May not detect MRD at very early stages due to limited sensitivity | Capable of detecting MRD at earlier stages, offering a potential advantage in timely intervention |
| Cost and speed | Cost and turnaround time can vary; some methods may be both time-consuming and expensive. | Emerging evidence suggests potential for a more cost-effective and rapid detection method, though further validation is ongoing. |
| Recommended sensitivity threshold | Generally, a threshold of at least 10-4 is required for reliable assessment. | Studies suggest that thresholds as low as 10-6 might correlate with prolonged progression-free survival, warranting further research and validation. |