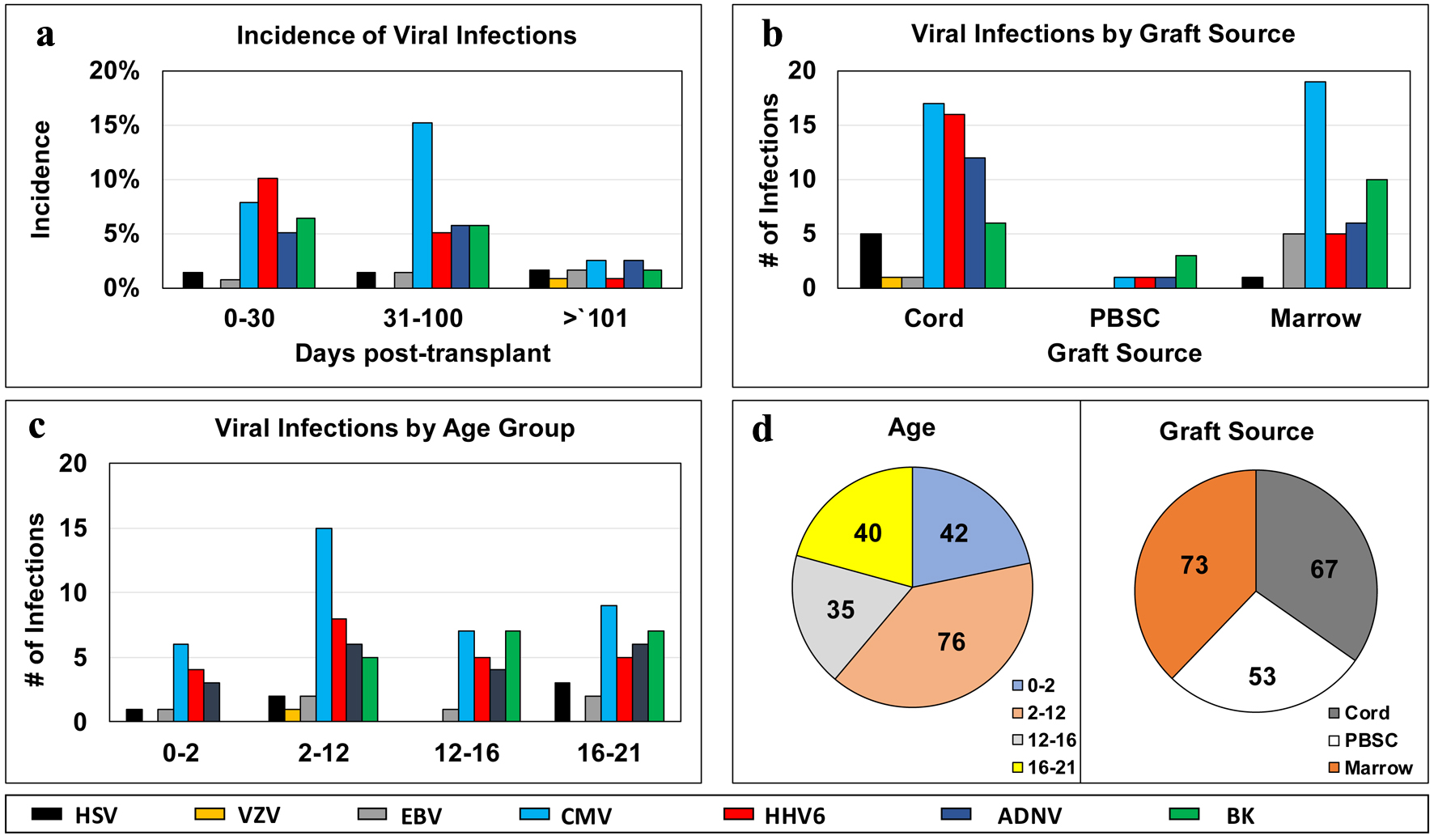
Figure 1. Distribution of infectious episodes by virus, along post-transplant phases (a), graft sources (b), age groups (c); and pie charts of distribution of viral infection episodes by age groups or graft sources (d). ADNV: adenovirus; BK virus: human polyoma virus 1; BM: bone marrow; CMV: cytomegalovirus; EBV: Epstein-Barr virus; GvHD: graft-versus-host disease; HHV6: human herpes virus 6; HSV: herpes simplex virus; PBSC: peripheral blood stem cell; pHSCT: pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant; UCB: umbilical cord blood; VZV: varicella-zoster virus.